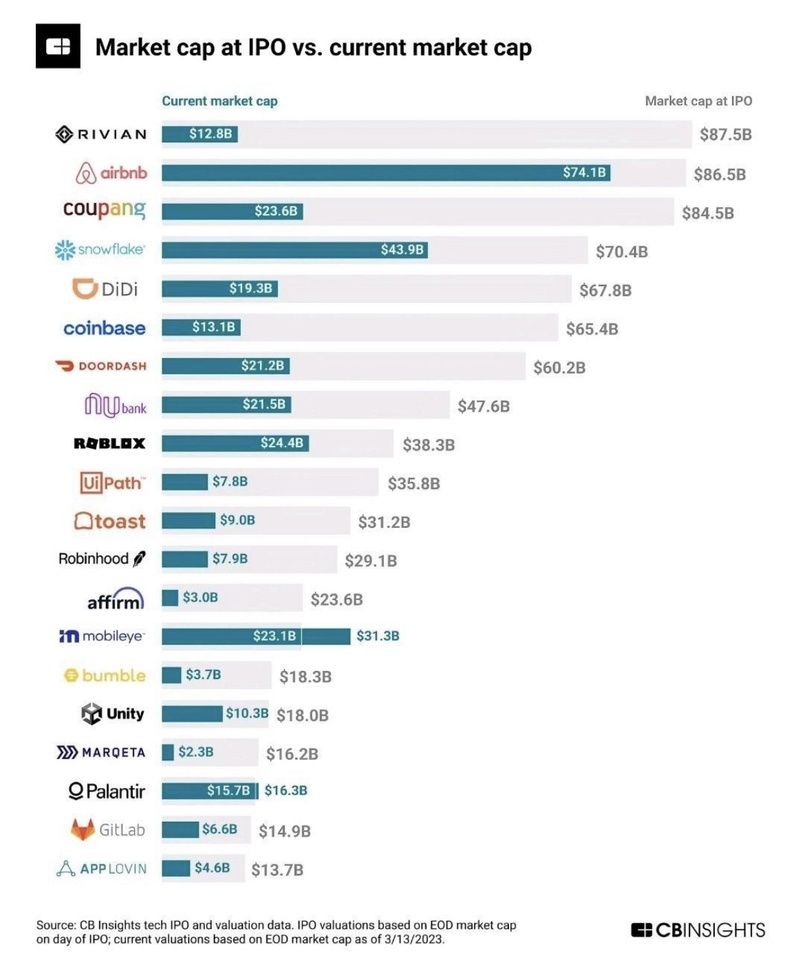
🚨 Beware of investing in the next big thing...
Source: CB Insights
$RIVN (-2.87%)
$ABNB (+0.97%)
$CPNG (-4.49%)
$SNOW (+2.95%)
$COIN (+2.18%)
$NU (+0.66%)
$RBLX
$PATH (-2.01%)
$HOOD (-1.11%)
$AFRM (-4.11%)
$PLTR (+1.49%)

Posts
19🚨 Beware of investing in the next big thing...
Source: CB Insights
$RIVN (-2.87%)
$ABNB (+0.97%)
$CPNG (-4.49%)
$SNOW (+2.95%)
$COIN (+2.18%)
$NU (+0.66%)
$RBLX
$PATH (-2.01%)
$HOOD (-1.11%)
$AFRM (-4.11%)
$PLTR (+1.49%)


Affirm
$AFRM (-4.11%) secures the largest largest capital commitment in its history.
In a new partnership with the private credit firm Sixth Street the latter is investing in loans worth 4 billion US dollars over three years, reports CNBC.
Graphic: affirm.com

All these stocks hit new 52 WEEK HIGHS at some point today
Apple $AAPL (-1.69%)
Affirm $AFRM (-4.11%)
Brookfield $BN (-5.98%)
Dutch Bros $BROS
Citi $C (-2.38%)
Cameco $CCO (-2.89%)
Carnival $CCL (+0.6%)
Marvell $MRVL (-3.8%)
Norwegian $NCLH (-0.08%)
On Holding $ONON
Palantir $PLTR (+1.49%)
Royal Caribbean $RCL (-0.54%)
Rocket Lab $RKLB (-4.55%)
Shake Shack $SHAK (-2.41%)
Square $SQ (-4.69%)
Trade Desk $TTD (-1.27%)
Visa $V (-1.41%)
Walmart $WMT (+1.57%)
$AFRM (-4.11%) | Affirm Q1 Earnings Highlights:
🔹 Revenue: $698M (Est. $664M) 🟢; UP +41% YoY
🔹 EPS: -$0.31 (Est. -$0.45) 🟢
🔹 GMV: $7.6B; UP +35% YoY
🔹 RLTC: $285M; Maintains 3.8% margin relative to GMV
Guidance:
🔹 Q2 Revenue: $770M-$810M (Est. $785M) 🟢
🔹 FY25 Revenue: $3.04B (Est. $3.02B) 🟢
Key Operational Metrics:
🔹 Adj Operating Income: $130M; margin of 18.6%
🔹 Active Consumers: 19.5M; UP +21% YoY
🔹 Active Consumers: 19.5M; UP +21% YoY
🔹 Transactions per Active Consumer: 5.1 vs. 4.1 YoY
🔹 Active Merchants: 323,000; UP +21% YoY
🔹 Total Transactions: 27.2M vs. 18.8M in Q1 FY2024
Credit Performance:
🔹 Delinquency Rates: Slight increases in 30+, 60+, and 90+ day categories due to credit seasonality and expanded loan approvals
Strategic Highlights and Initiatives:
🔸 Affirm Card Growth: Over 1.4M active cardholders; GMV per user exceeding $3,000
🔸 Product Expansion: Launched in the UK, integrated with Apple Pay, and expanded partnerships with Shopify and WooCommerce
🔸 Funding Capacity: Increased to $16.8B; Authorized convertible debt repurchase of up to $500M for 2025
CEO Max Levchin’s Commentary:
🔸 "Shop Pay Installments, powered by Affirm, has surpassed $10B in cumulative GMV. We're excited to deepen our joint initiatives with Shopify, including off-Shopify Shop Pay."
Affirm Q3 2024 $AFRM (-4.11%)
Financial performance:
Balance sheet overview:
Income details:
Cash flow overview:
No specific details on cash flow have been provided in these reports.
Key ratios and profitability metrics:
Competitive position:
Affirm recorded competitive delinquency rates on loans over 30 days compared to other consumer lenders. This demonstrates a strong position in managing credit risk and supports confidence in Affirm's risk management practices.
Forecasts and management commentary:
Risks and opportunities:
Summary of results:
Positives:
Sales growth: Sales increased by 41% compared to the previous year, showing strong business expansion.
Improved operating profit: Operating profit improved by USD 77 million, highlighting efficiency in cost management.
Increased adjusted operating margin: Margin increased to 19%, providing Affirm with a healthier financial position.
Successful pricing strategy: Pricing initiatives resulted in higher interest income and improved monetization.
Competitive credit quality: Lower default rates positively differentiate Affirm from other lenders.
Negative aspects:
Net deficit: Despite improvements, Affirm remained in deficit with a net loss of $100 million.
High operating expenses: The cost of corporate guarantees and share-based payments weighed on the result.
Increased provisions: Provisions increased due to higher loan origination and timing of loan sales.
Low growth due to new initiatives: Product launches and market expansions are not expected to make a significant contribution to growth in the 2025 financial year.
Economic risks: Potential impact from economic uncertainties and interest rate changes could affect demand and profit margins.

Affirm
$AFRM (-4.11%) has announced its first international expansion and launched its "Buy Now, Pay Later" service in the United Kingdom 🇬🇧 - CNBC.
Photo: Yahoo

INITIAL MARKET REACTION TO TRUMP VICTORY:
Earnings next week
$$BRK.A (-1.07%) (Saturday)

Part 2:
The evolution of embedded finance: banks at a crossroads
Reading time: approx. 4 minutes
The emergence and growth of embedded finance have presented banks around the world with a strategic decision: Do they give up "simple" payments and payment processing and focus on more more complex services such as asset management, M&A and IPOs? Or do they continue to build the financial infrastructure to keep pace with fintechs and tech companies?
To grasp the deep understanding of embedded finance and the role of banks, we need to analyze the change in the financial world and the shift in power between traditional banks and tech giants.
Embedded finance: redefining the role of banks
Historically, banks have been banks were not only the main players in the provision of financial products, but also the sole point of access to these services. However, the digital revolution, led by tech giants and fintechs, has profoundly changed the relationship between bank and customer. Embedded financewhich enables the seamless integration of financial services into digital platforms, poses a major challenge for banks.
Technological platforms take over payment processing: Companies such as Stripe, Adyen and Square offer comprehensive payment infrastructures that enable platforms to offer financial services without the direct involvement of a bank. These companies are often faster, more flexible and, above all, cheaper than traditional banks.
Banks as infrastructure providersSome banks have opted to take on a strategic role in the background. They provide the infrastructure for payments and loans but leave the customer experience to the platforms. Examples of this are banks such as Hypothekarbank Lenzburgfintechs such as neon to offer banking services without having a banking license themselves.
Retreat into more complex services: On the other hand, there are banks that specialize in high-quality, advisory-intensive services such as asset management, IPOs and M&A transactions focus. These services require deep expertise, regulatory experience and trust - factors that tech companies struggle to replicate.
Which direction are banks taking?
Banks are faced with a strategic choice between (mainly) two models:
1.) Becoming an infrastructure provider:
Some banks no longer want to be the central interface to the customer, but focus on providing a robust infrastructure. BBVA and Goldman Sachs for example, have started to provide their infrastructure via Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) to other companies. They provide platforms with the necessary financial tools without being in the foreground. The advantage: they can earn money from a growing number of transactions without competing directly with tech companies.
Advantages for the banks:
Disadvantages:
2) Focus on advisory-intensive services:
Another group of banks is focusing on high-value financial servicesthat require personalized advice and specific know-how. The UBS is an example of this. By withdrawing from the mass business with simple payments and loans, it can concentrate on asset management and corporate finance where margins are higher and there is less competition from tech companies. The divestment of "Swisscard" to AmericanExpress may be an indication that UBS wants (or needs?) to focus on its core business.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Technological change and competitive pressure
A key driver of this change is the technologization of the financial sector. APIs enable platforms such as Amazon, Airbnb or Shopifyto offer financial services without a bank in the foreground. These developments have not only made the banking market smaller, but have also put pressure on bank margins increased.
One example of the influence of embedded finance is the shift in credit and payment options. Klarna offers "Buy Now, Pay Later" (BNPL) models directly at the checkout of online retailers. Although the customer thinks they are paying the merchant directly, the actual credit processing takes place in the background via Klarna. The merchant receives their money immediately, and Klarna earns from the customer's installment payments. This underlines how tech companies have taken over the traditional model of the credit business without being a bank themselves.
Banks at a crossroads?
The future of banks will depend heavily on the strategic decisions they make. The The loss of direct customer contact in payment transactions through embedded finance is a challenge, but banks can use this change to either focus on infrastructure or high-value services specialize in either infrastructure or high-value services. However, both require massive investments in technologyto remain competitive.
In the next part of the series, we take a closer look at how the technologies behind embedded finance work and how banks and companies can use these systems efficiently to consolidate their position in the market.
Let me know what you think! - Leave a comment!
Happy investing! 😊
GG
$AXP (-2.55%)
$UBSG (-2.01%)
$ADYEN (-0.8%)
BONUS:
The global embedded finance market in 2023 was estimated at USD 83.32 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 32,8% further growth. This growth is due to the increase in smartphones and internet access worldwide.
Stay tuned, the series continues! ♥️🔥
$PYPL (-4.23%)
$GOOGL (-0.59%)
$GOOG (-0.71%)
$AMZN (-1.09%)
$PYPL (-4.23%)
$AFRM (-4.11%)

Top creators this week